For the OS practical assignment we decided to implement a simulation of the MMU, in python programming language. In this post, I will show the code, an explanation of it, and screen captures of the results.
Page Table
As we already know, the page table is used to do memory translations from logic to physical addresses which are understandable to the drivers.
To begin, the script has as parameters first, the size of the address range, namely, the number of bits the computer has to assign addresses. The second is the size of the main memory, and the third the frame size.
The script starts verifying the parameters, to check if they meet certain conditions. Then some of these values are passed as attributes of the class PageTable and calculates the number of bits belonging to the logical address to get an idea of how many rows the page table will need.
Now to generate the page table, we use a "for" to add to a matrix the rows of the Page Table. To tell how many rows it must add, it uses the value from the logical addresses and raises the 2 to the power of that number. Maps the frames of the main memory, and when it ends, maps it again in the spare addresses, with this we achieve that any accessed logical address will have an assigned physical address.
def __init__(self, tamDireccionVirtual, memoriaP, tamFrame):
if (memoriaP%2 != 0) or \ # El tamaño de la memoria principal debe ser un multiplo de 2
(tamFrame%2 != 0) or \ # El tamaño de las frame debe ser un multiplo de 2
( memoriaP%tamFrame != 0) or \ # El tamaño de la memoria principal debe ser un multiplo de el tamaño de la frama
( pow(2,tamDireccionVirtual) < tamFrame) or \ # El tamaño del frame debe poder contenerse en el rango de direcciones
( tamDireccionVirtual%4 != 0): El rango de direcciones debe ser multiplo de 4
print 'Error'
return
self.tDVirtual = tamDireccionVirtual; # bits
self.ram = memoriaP # bytes
self.tFrame = tamFrame # bytes
self.numeroMaximoFrames = 300
#[Direccion fisica, bit de presencia, bit de persistencia, dirty bit, lectura, escritura, modificacion]
self.pageTable = []
# Calcular el numero de direcciones logicas que se pueden tener
self.numDireccioneslogicas = self.tDVirtual - math.log(self.tFrame,2)
# Generar la page table
print 'Numero de registo logico direccion fisica'
contadorDirFis = 0 # Este contador es utilizado para asignar las primeras direcciones a la memoria principal en la tabla
for i in range(0, (int( pow( 2,self.numDireccioneslogicas)) - 1) ):
if i < self.ram/tamFrame :
self.pageTable.append([contadorDirFis, 1,0,0,0,0,0])
else:
self.pageTable.append([contadorDirFis, 0,0,0,0,0,0])
if( contadorDirFis < (self.ram-self.tFrame) ):
contadorDirFis = contadorDirFis + self.tFrame
else :
contadorDirFis = 0
print "%s %s"%(i,self.pageTable[i])
print 'Page table creada.'
The result is the following:
The Page Table is in charge of translating addresses, so to achieve this, the method obtenerDireccionFisica receives a String parameter with a hexadecimal logical address of a certain size. The method splits the address and gets from it the address of the page in the table and the displacement in memory inside of it, and converts it into an integer.To finish, the method searches for the page in the table, and verifies that this page is found on the main memory, otherwise it raises a "Page Fault".
def obtenerDireccionFisica(self, direccionLogica ):
direccionFisica = direccionLogica[0 : int(self.numDireccioneslogicas/4)] # Parte la direccion logica y obtiene la direccion del frame en la tabla
# Parte la direccion logica y obtiene la direccion de desplazamiento de la frame
desplazamiento = direccionLogica[int(self.numDireccioneslogicas/4) : int(self.tDVirtual /4)]
if self.pageTable[int(direccionFisica, 16)][1] == 1: "Verifica que se encuentre en la memoria principal
return self.pageTable[int(direccionFisica, 16)][0] + int(desplazamiento, 16) # Convierte las direcciones a hexagesimal y obtiene la direccion
else:
return "Page fault"
The result is the following:
TLB
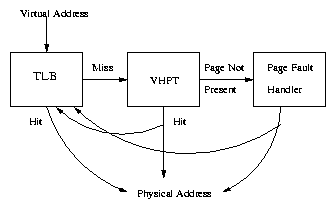
The TLB works as a cache memory to translate quicker the last used addresses, this memory is pretty quick, and all the rows are accessed simultaneously, which makes it more useful, the problem is, this memory is very small, so it works together with the Page Table to translate addresses.
The TLB receives as parameters the Page Table and the quantity of rows the TLB cache has, then it builds it using the first rows of the Page Table.
def __init__(self, PageTable, filas):
self.pt = PageTable
self.filas=filas
self.table=[] #[ direccion de pagina, PID, sin usar, direccion fisica, N, D, V, G, vejes]
for i in range(0,self.filas):
self.table.append([i, 0, 0, self.pt.pageTable[i][0],0,0,0,0, 0])
print " {} {}".format(i, self.table[i])
print 'TLB creada'
Result:
To get the physical address, first the TLB splits the logical address in the page address and the displacement, then with a "for" cycle, searches if this address is in the TLB, if it is not there, it searches in the Page Table.
It is important to note, the page table must know which pages bring out, and which bring in the Page Table. For this every row has an "age" number which increments every time a page is brought to the TLB, so when it is necessary to take out a page, the TLB uses this number as an index to decide which one bring out, taking out one of the oldest pages.
def obtenerDireccionFisica(self, direccionLogica ):
direccionDePagina = int( direccionLogica[0 : int(self.pt.numDireccioneslogicas/4)] , 16)
desplazamiento = int( direccionLogica[int(self.pt.numDireccioneslogicas/4) : int(self.pt.tDVirtual /4)] , 16)
vejes = 0
for i in range(0,self.filas):
if vejes < self.table[i][8] :
vejes = self.table[i][8]
for i in range(0,self.filas):
if( self.table[i][0] == direccionDePagina):
print 'Direccion encontrada en la tlb'
for e in range(0,self.filas):
self.table[e][8] = self.table[e][8] + 1
return self.table[i][3] + desplazamiento
print 'Direccion no encontrada en la tlb, buscando en la page table y actualizando la tlb ...'
resultado = self.pt.obtenerDireccionFisica( direccionDePagina, desplazamiento)
if resultado != "Page fault" :
for i in range(0,self.filas):
if vejes == self.table[i][8] :
for e in range(0,self.filas):
self.table[e][8] = self.table[e][8] + 1
self.table[i] = [direccionDePagina, 0, 0, self.pt.pageTable[direccionDePagina][0],0,0,0,0, 0]
self.pt.pageTable[direccionDePagina][1] = 1
break
return resultado
else:
print "Se ha generado un {} moviendo datos y actualizando la tlb...".format(resultado)
for i in range(0,self.filas):
if vejes == self.table[i][8] :
for e in range(0,self.filas):
self.table[e][8] = self.table[e][8] + 1
self.table[i] = [direccionDePagina, 0, 0, self.pt.pageTable[direccionDePagina][0],0,0,0,0, 0]
self.pt.pageTable[direccionDePagina][1] = 1
break
return self.pt.pageTable[direccionDePagina][0] + desplazamiento
Resultado: